In various promotions of water pumps, we often see introductions to motor grades, such as "Level 2 energy efficiency", "Level 2 motor", "IE3", etc. So what do they represent? How are they classified? What about the judging criteria? Come with us to find out more.

Figure | Large Industrial Motors
01 Classified by speed
The nameplate of the water pump is marked with the speed, for example: 2900r/min, 1450r/min, 750r/min, these speeds are related to the classification of the motor. Motors are divided into 4 levels according to this classification method: two-pole motors, four-pole motors, six-pole motors and eight-pole motors. They have their own corresponding speed ranges.
Two-pole motor: about 3000r/min; four-pole motor: about 1500r/min
Six-pole motor: about 1000r/min; eight-pole motor: about 750r/min
When the motor power is the same, the lower the speed, that is, the higher the number of poles of the motor, the greater the torque of the motor. In layman's terms, the motor is more powerful and powerful; and the higher the number of poles, the higher the price. In compliance with the requirements In working conditions, the lower the number of poles is selected, the higher the cost performance.

Figure | High speed motor
02 Classified by energy efficiency
Energy efficiency grade is an objective standard for judging the energy utilization efficiency of motors. Internationally, it is mainly divided into five grades: IE1, IE2, IE3, IE4, and IE5.
IE5 is the highest grade motor with a rated efficiency close to 100%, which is 20% more efficient than IE4 motors of the same power. IE5 can not only save energy significantly, but also reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
IE1 is an ordinary motor. Traditional IE1 motors do not have high-efficiency performance and are generally used in low-power application scenarios. They not only consume high energy but also pollute the environment. Motors of IE2 and above are all high-efficiency motors. Compared with IE1, their efficiency has increased by 3% to 50%.

Figure | Motor coil
03 National standard classification
The national standard divides energy-saving water pumps into five levels: general type, energy-saving type, high-efficiency type, super-efficient type, and stepless speed regulation type. In addition to the general type, the other four grades need to be suitable for various lifts and flows, which tests the versatility of the energy-saving water pump.
In terms of energy efficiency, the national standard also divides it into: first-level energy efficiency, second-level energy efficiency, and third-level energy efficiency.
In the new version of the standard, the first-level energy efficiency corresponds to IE5; the second-level energy efficiency corresponds to IE4; and the third-level energy efficiency corresponds to IE3.
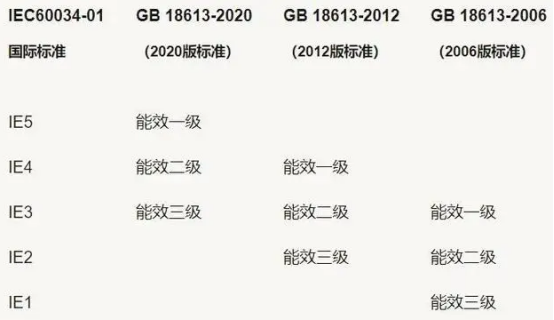
Figure | Comparison of energy saving standards
There are many classification methods for motor energy efficiency, all of which are standards for judging energy saving and consumption reduction.
Follow Purity Pump Industry to learn more about water pumps!