Vertical Inline Centrifugal Pumps are a crucial component in numerous industrial and commercial applications, especially in environments where space is at a premium. These pumps are known for their compact design and efficient operation. This article will delve into their design and working principles, types, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and common troubleshooting issues.
Design Features:
Vertical inline centrifugal pumps are characterized by their suction and discharge ports aligned with the piping system, designed specifically for vertical installation. This alignment ensures a smooth flow of the pumped liquid, making them ideal for small pump rooms and other confined spaces. These pumps are primarily used to transport low-viscosity fluids like water and certain chemicals, and they are commonly found in circulator pump applications where pressurized water flow is needed.
Working Principle:
The operation of a vertical inline centrifugal pump is based on the forced vortex principle. When the electric motor is started, it rotates the impeller, creating a vacuum within the pump casing. This vacuum draws liquid into the pump through the suction port. The liquid is then subjected to centrifugal force as it passes through the spinning impeller, which moves it radially and axially outward. Upon exiting the impeller, the liquid enters the diffuser where its velocity decreases and pressure increases. Finally, the liquid is directed through the pump outlet and into the piping network for transfer to the desired location.

Picture|Purity vertical inline centrifugal pump-PTD
Monoblock Vertical Inline Pumps:
Monoblock VILs feature an impeller directly connected to the motor shaft, making them simple and cost-effective, though maintenance can be challenging. They are suitable for light-duty tasks and short operation periods at full motor speed.
Rigid-Coupled Vertical Inline Pumps :
These pumps have separate motor and pump shafts connected by a rigid coupling. This design is robust and easier to repair, making them suitable for applications requiring high strength and stability.
Spacer-Coupled Vertical Inline Pumps :
In spacer-coupled VILs, the motor shaft is connected to the pump head via a flexible coupling that includes an additional bearing assembly. This design accommodates minor misalignments and ensures even distribution of radial loads, making these pumps easy to maintain and ideal for applications with short maintenance cycles and low downtime, such as fire pumps and boiler feed pumps.
Single-Suction Vertical Inline Pumps :
Single-suction VILs have a compact construction where the pumped liquid enters from one side of the impeller and exits from the other, ensuring smooth operation.
Double-Suction Vertical Inline Pumps :
Double-suction VILs feature a back-to-back impeller design, allowing fluid to enter from both sides and discharge from the middle. This design handles higher flow rates and reduces the risk of cavitation, making it suitable for more demanding applications.
Vertical inline centrifugal pumps are versatile and used in a variety of settings:
Agricultural Irrigation: Efficiently transporting water to fields.
Domestic and Industrial Water Transport: Moving water for various household and industrial purposes.
Cleaning and Industrial Recirculation Systems: Ensuring consistent water flow in cleaning operations and industrial processes.
Municipal Water Supply Systems: Pumping water in city infrastructures.
Air Conditioning and Heating Systems: Circulating water in HVAC systems.
Fire Protection: Serving as fire pumps in safety systems.
Boiler Feed Pumps: Supplying water to boilers.
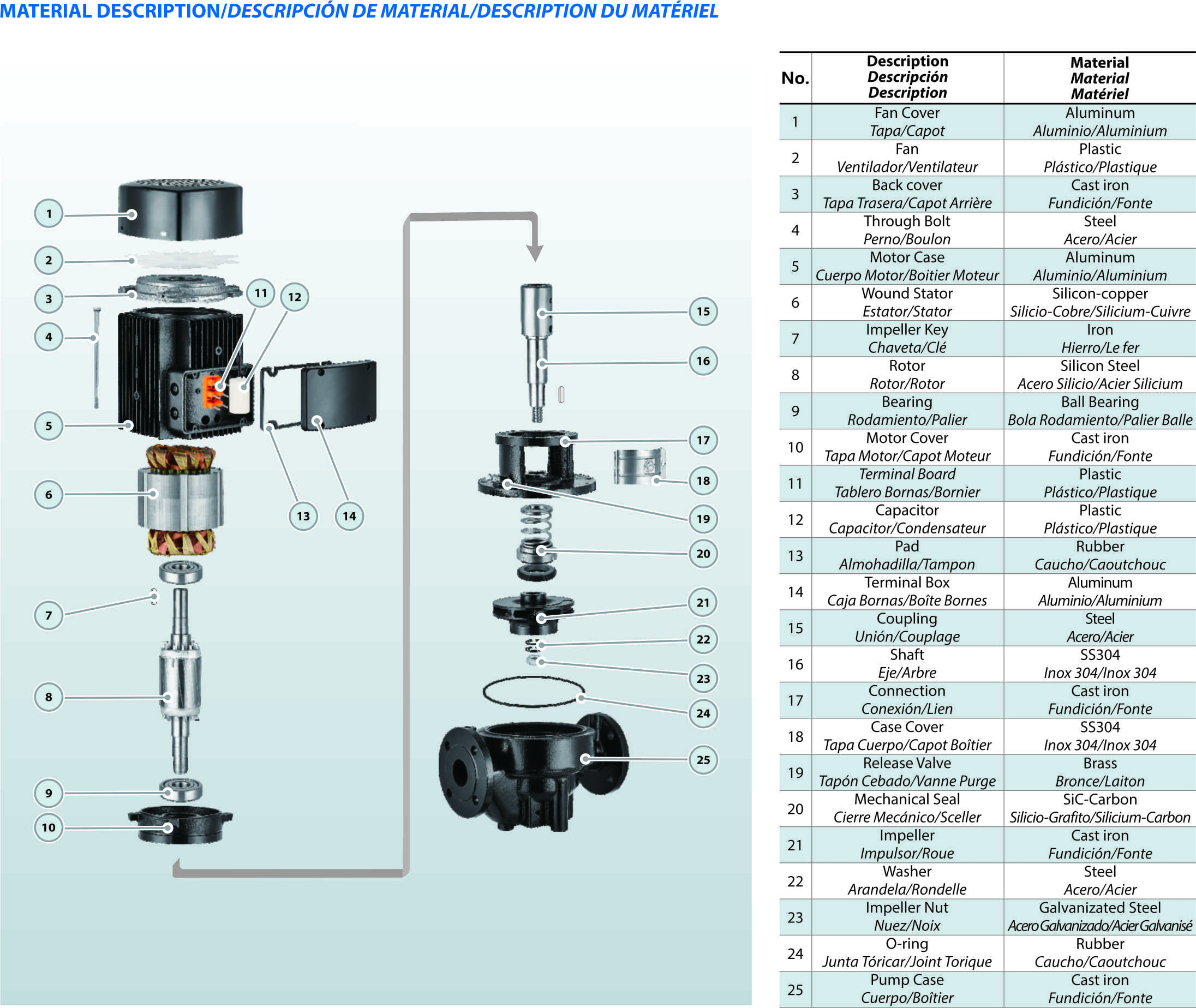
Picture|PTD Parts Diagram
Advantages:
1. High Efficiency: VILs are energy-efficient and can handle high pressures and temperatures.
2. Space-Saving Design: Their compact structure requires less floor space, with the motor and service clearance above the pump casing.
3. Easy Installation: Simplified piping network and monoblock design eliminate the need for coupling and shaft alignment.
4. Low Noise and Vibration: Vertical shafts are naturally balanced, reducing operational noise and vibration.
Disadvantages:
1. Vertical Clearance Requirement: Installation and maintenance require significant vertical space.
2. Maintenance Complexity: Servicing mechanical seals and handling corrosion issues can be challenging, especially for large motors exceeding 25 hp.
Zero Discharge:
Check for blockages in the inlet.
Ensure the motor rotation direction is correct.
Remove any air in the pump or suction pipework.
Clear any blockages in the impeller or check valves.
Excessive Vibration:
Inspect and replace worn-out impellers.
Rebalance unbalanced components.
Correct any obliquities or imbalances in the pump shaft.
High Noise Levels:
Replace worn-out bearings or impellers.
Address cavitation issues by ensuring the suction pressure head is adequate.
Confirm the pump is operating within the specified duty range.
Tighten any loose components.
Bearing Overheating:
Correct coupling alignment.
Maintain proper lubricating oil levels and cleanliness.
Drain excess grease from the bearing housing.
Driver Overload:
Reduce pump speed if too high.
Check for mechanical obstructions or deflections.
Ensure the liquid density and viscosity are within pump design specifications.
Verify the voltage supply to the pump.
Vertical inline centrifugal pumps are essential for various industrial and commercial applications due to their compact, space-saving design, high efficiency, and reliability. Despite their complex maintenance requirements, they remain a preferred choice in many critical applications, offering a balance of performance and practicality.